Poster: Free intra-abdominal gas - where did it come from?
Perforated gastric or duodenal ulcer
Perforation of a peptic ulcer is the most common cause of pneumoperitoneum.
Anterior wall ulcers of the stomach and duodenal bulb usually perforate freely into the intraperitoneal space, initially supramesocolic, whereas posterior wall gastric ulcers perforate into the lesser sac.
Some ulcers will seal off immediately, the only radiological sign of perforation may be a small locule of gas adjacent to the stomach or in the gastroduodenal ligament.
NHÂN CA THỦNG LOÉT HÀNH TÁ TRÀNG TẠI MEDIC
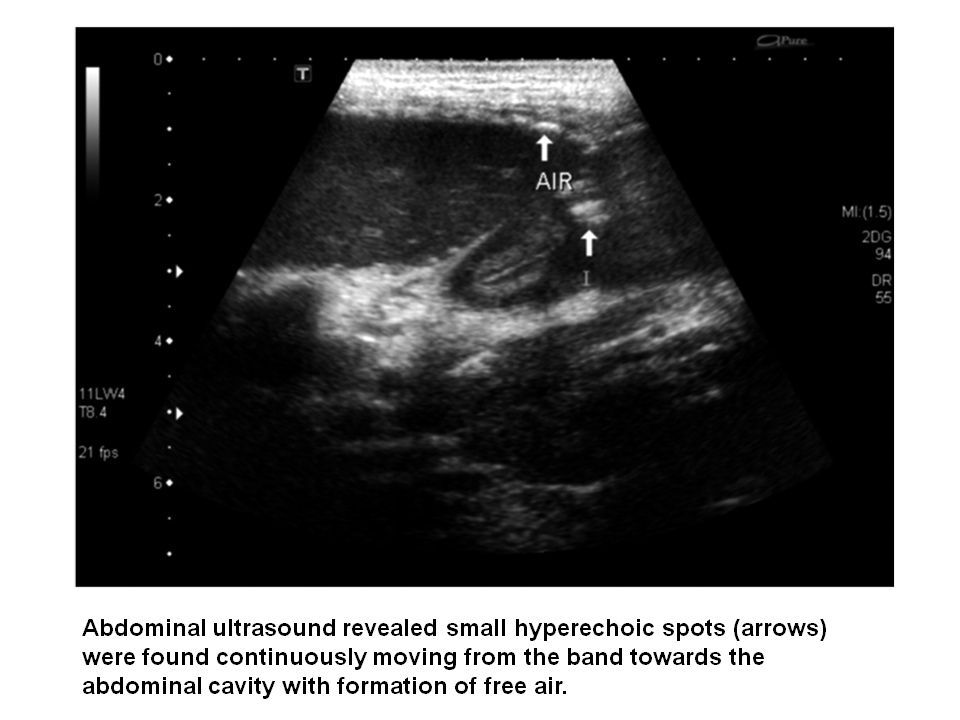
Sonographic findings suggestive of peptic ulcer perforation
include the presence of ascites, intraperitoneal free air and a linear
echogenic band transversing the entire bowel wall.





Không có nhận xét nào :
Đăng nhận xét