Trong số 20 ca lymphom lan tỏa dòng tế bào B lớn [diffuse large B cell lymphoma] ở Trung tâm Y khoa Medic từ 2008, có 03 ca có triệu chứng đau răng và hàm mặt điều trị giảm đau, nhổ răng..không bớt, sau đó xuất hiện nhiều tổn thương khác ngoài hạch. Trong khi đó, tìm được một bài báo về đau xương hàm dưới trong lymphom ác. Sau đây là một hồi cứu về đề tài này.
and Appearences in Oral Cavity, and Maxillary Area
Nguyen Thien Hung,
Jasmine DCB Thanh Xuan, Le van Tai, Le
Thong Nhat, Le Thanh Liem, Phan Thanh Hai
Medic
Medical Center, HCMC, Vietnam
INTRODUCTION:
May there had been an initial symptom in oral cavity, maxillary
and mandibular area for diffuse infiltration of lymphoma? We will represent some cases of diffuse
lymphoma with appearences in oral
cavity, and maxillary areas.
MATERIALS and METHODS:
We retrospectively reviewed
20 cases of diffuse lymphoma that were histopathologically diagnosed in
our center from 2008 in which presented 03 cases with oral cavity, maxillary symptoms and bone
involvement [01 case in male 42 yo and 02 cases in female gender, 33 and 40 year-old].
RESULTS:
CASE 1= A 33 year-old female patient with pain in lower maxillary bone for one month and
tension in both 2 breats), hyperpigmented edema of areolar area both 2
sides without pregnancy. ABVS scanning
detected multiple nodules infiltrating in 2 breasts.
Biopsy of 2 breasts
reported microscopic with immunohistochemistry scanning, diffuse large B cell lymphoma.
MRI full body with gado
detected bone marrow changing, 2 breats hypercaptured
contrast, ascites and kidney infiltration. In pelvis 2 ovarian
tumors and big uterine cervix were detected. Blood tests showed lower
platelets, EGFR lower 46, beta2 microglobuline raised
3816, ferritin raised 911, LDH-l raised 1360.
CASE 2= A 40 year-old female patient with toothache but pain
remained after removing tooth, and in total body examination detected right
pleural effusion and some nodular tumors
in thyroid, left breast and subcutaneous area of right neck, left chest all
and lumbar region. Erosions of left
clavicle and right 1st rib. Biopsy of left breast tumor reported diffuse large B cell lymphoma.
CASE 3= Man 42 year-old, one month ago,
pain in oral sinus, difficult eating and 2 days after, pain appears in
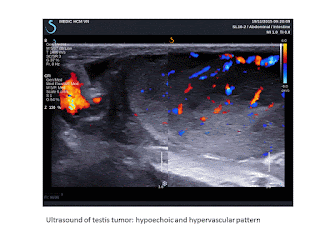
left testis. Ultrasound of left big and hot testis represented hypoechoic
infiltration, hypervascular of one
part of testis and elastoscan ultrasound value # 10.5 kPa).
DISCUSSION:
There are published reports of pain in mandibular area as initial symptom
but symptoms in oral cavity and maxillary bone as onset symptom seems to be not
represented in literature. But it exists a case of pain in oral cavity for
lymphoma infiltrating in testis and an another case of pain in maxillary area
for lymphoma in whole body in this report.Toothache and pain in maxillary region remained with management guided a survey in all body and detected extranodal
CONCLUSIONS:
Seveval reports of
lymphoma in mandible were published with pain as initial symptom, but in cases of diffuse infiltration of
lymphoma in whole body, the appearences in oral cavity, maxillary and mandibular
areas with pain symptom may be added criteria of diagnosis for lymphoma in
clinical examination.
REFERENCE
Mochizuki, Y., Harada, H., Sakamoto, K., Kayamori, K., Nakamura, S., Ikuta, M., Kabasawa, Y., Marukawa, E., Shimamoto, H., Tushima, F. and Omura, K. (2015) Malignant Lymphoma with Initial Symptoms in the Mandibular Region. Journal of Cancer Therapy, 6, 554-565
Abstract
Primary intraosseous lymphoma is rare and there are few case reports manifesting with a mass in the mandible. Thus, we retrospectively reviewed and analyzed the clinical characteristics, treatment, and outcome of extranodal non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) with initial mandibular symptoms in our department. At initial treatment of dental clinics, dentists had diagnosed as dental or gingival diseases and had performed dental treatment. Neurological disorder to involvement of the inferior alveolar nerve was present in 80.0% of our cases. On dental or panoramic radiography a specific radiolucent lesion in the mandible was not detected, except for dental lesions. On CT, NHL of the mandible region has no widening and no clear destruction but a slit-like the cortex bone destruction pattern with keeping in shape of the mandibular body (62.5% of CT-examined cases), and extraosseous soft tissue mass are clearer on MRI (100.0% of MRI-examined cases).
Histopathologically, 80.0% of our cases were diagnosed as diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
One case as B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma and one case as B-cell lymphoma unclassifiable with features intermediate between DLBCL and Burkitt lymphoma were Stage IV (Ann Arbor staging system) and had poor prognosis. The disease-specific survival rate was 77.8% at 5 years. If unexplained non-specific symptoms such as swelling of the jaw, pain, neurological disorder of the inferior alveolar nerve, tooth mobility are observed, oral surgeons and dentists should not perform
dental treatments. CT and MRI show disease specific appearance to be able to give a definitive diasnosis as NHL. PET/CT is useful for scaninng of whole body. A deep bone biopsy is preferred for
suspected malignant lymphoma.








Không có nhận xét nào :
Đăng nhận xét