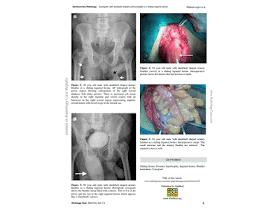
Chẩn đoán trước mổ chủ yếu là siêu âm và chụp cản quang bàng quang ngược dòng, với hình bàng quang thoát vị dạng quả tạ [dumbbell shaped urinary bladder]; chẩn đoán đúng gíup tránh làm rách bàng quang khi mổ khâu thoát vị bẹn [herniorhapphy].
J Radiol
Case Rep. 2009;3(2):7-9. doi: 10.3941/jrcr.v3i2.91. Epub
2009 Feb 1.
Cystogram
with dumbbell shaped urinary bladder in a sliding inguinal hernia.
Author
information
Abstract
Sliding inguinal hernias present with various
symptoms and these are usually direct inguinal hernias containing various
abdominal viscera. Case reports and series have been published with various
organs and rare organs being part of the hernia. Urinary bladder is a known
content of sliding hernias. This case report emphasizes this aspect in a
picturesque manner and the importance of radiological investigations for
pre-surgical evaluation.
KEYWORDS:
Bladder herniation; Cystogram; Inguinal hernia; Prostatic
hypertrophy; Sliding hernia
[Bladder hernia]. Ann Ital
Chir. 1995 May-Jun;66(3):363-9.
Abstract
A case of bladder hernia
in a 61 years old patient affected by benign prostatic hypertrophy is
presented. Pre-operative diagnosis was made by cystography. After an
adenomiomectomy of the prostate, the patient underwent the resection of the
herniated bladder which gave the bladder its normal shape with only a slight
reduction of its capacity. Inguino-scrotal bladder hernias are very rare;
recognized predisponing factors are weakening of muscular and connective
structures of the inguinal canal, and bladder hypotonia secondary to
urethro-prostatic obstruction.
These hernias, according
to the anatomical position of the hernial sac, bladder and peritoneum, are
classified in paraperitoneal (most frequent), intraperitoneal and
extraperitoneal. The typical symptom of this disease is the two-stage
micturition: the patient after a first spontaneous voiding, presses the mass
and voids again. Other than cystography, useful diagnostic means are urography
and cystoscopy which may confirm the diagnosis and rule out associated urinary
disease.
The treatment consists
of either simple reduction of the bladder hernia, if the hernia is small, or
resection of the herniated portion of the bladder, if the hernia is large or is
associated with other diseases (e.g. tumors). Bladder resection is then
followed by closure of the bladder wall in two layers and by inguinal hernia
repair.
Actas Urol Esp. 1999
Jan;23(1):79-82.
[A massive hernia of the
bladder into the scrotum. A report of a case].
[Article in Spanish]
Ojea Calvo A1, Rodríguez Alonso A, Pérez García D, Domínguez Freire F, Alonso Rodrigo A, Rodríguez Iglesias B, Benavente Delgado J, Barros Rodríguez JM, Nogueira March JL.
Abstract
The hernia of the
bladder in the scrotum is a highly uncommon observation. From the clinical
standpoint the usual manifestation is a two-stroke voiding. The recommended
urological examinations to reach a diagnosis are ultrasound, endovenous
urography, retrograde urethrocystography and cystoscopy. Management includes
the de-obstruction of the lower urinary tract, if present, resection of
associated peritoneum, resection or reduction of the vesical hernia and
repairment of inguinal path. The case contributed corresponds to a vesical
hernia in a 72-year-old patient, with no obstructive cause, that was treated
surgically by resection of the herniated bladder, with good morphological and
functional results.
Actas Urol Esp. 1997
May;21(5):514-8.
[Vesico-scrotal hernia. Report of
a clinical case].
[Article in
Spanish]
Author information
Abstract
Incidental discovery of vesical hernias
during herniorrhaphy is quite common. In such cases, patients are usually
asymptomatic since the hernia portion is small and easily repairable. On the
other hand, vesical solid protrusion to the scrotum is quite unusual, and is
generally found associated to obstructive urinary symptoms. Management involves
basically the correction of any associated obstructive conditions, correction
of the vesical hernia and herniorrhaphy.







Không có nhận xét nào:
Đăng nhận xét