FAST EXAM
The FAST exam is a specific ultrasound examination used by medical professionals to look for hemorrhage or abnormal fluid in the pericardium, pleural cavity, and peritoneal cavity after traumatic injury. The eFAST (extended FAST) exam is basically the regular FAST with additional views to examine the lungs. It’s a bedside ultrasound, which means the imaging equipment can be brought to where the patient is.
Peritoneum landmarks in Human Anatomy Atlas 2020
When a FAST/eFAST exam is being conducted, there are typically a few key views that focus on a number of important structures, such as particular organs and regions of the peritoneum.
The Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ) view “uses the liver as an ultrasound window” to look for fluid in the hepatorenal space (Morison’s pouch). The right subphrenic space, which lies between the liver and diaphragm, is another place fluid can accumulate. In addition, moving the ultrasound probe towards the head (cephalad) provides a view of the right pleural space and caudal movement provides a view of the right paracolic gutter.
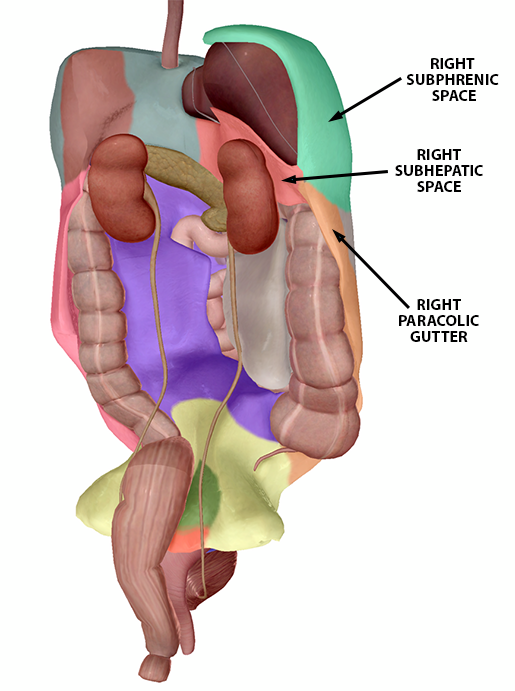 Right Upper Quadrant peritoneum landmarks (female model). Image from Human Anatomy Atlas.
Right Upper Quadrant peritoneum landmarks (female model). Image from Human Anatomy Atlas.
The Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ) view uses the spleen to look at the left subphrenic space (the space between the spleen and the diaphragm) and the splenorenal recess (the space between the spleen and left kidney). The left pleural space and left paracolic gutter can also be examined via movement of the probe.
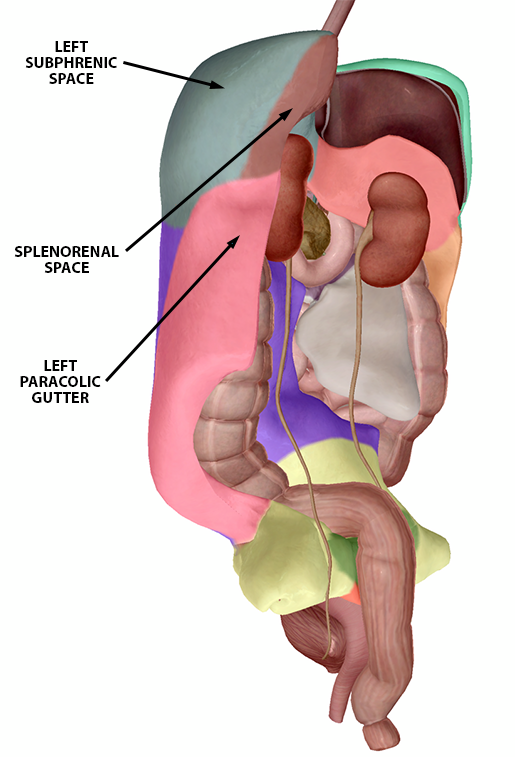
Left Upper Quadrant peritoneum landmarks (female model). Image from Human Anatomy Atlas.
The Pelvic view is used to examine the rectovesical recess or rectouterine recess. The rectovesical recess is the space between the rectum and the bladder in the male pelvis, while the rectouterine recess is the space between the rectum and the posterior uterine wall in the female pelvis.
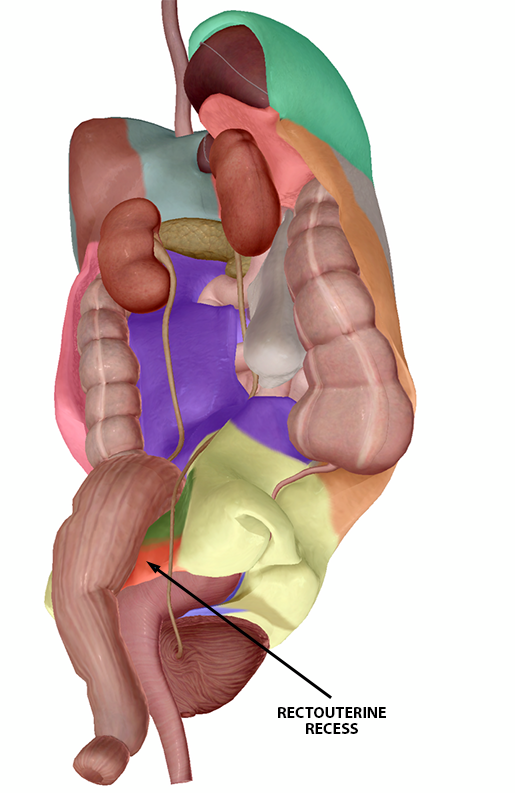
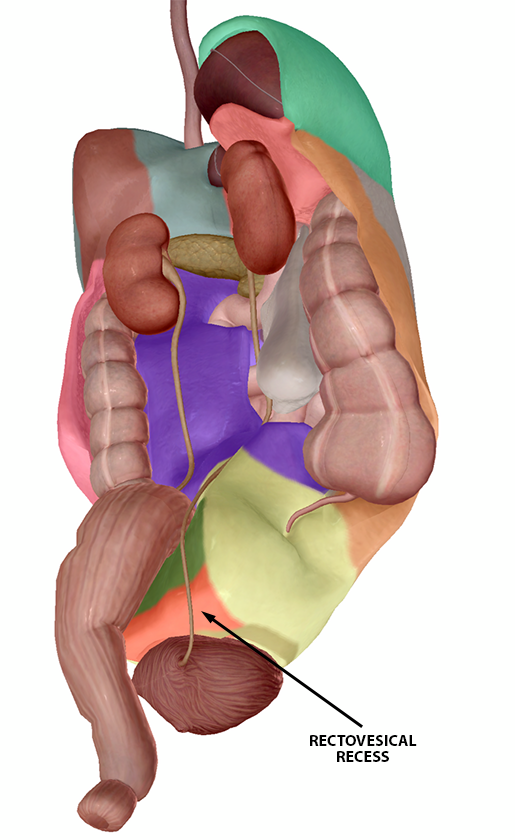
Rectouterine recess (f) and rectovesical recess (m). Images from Human Anatomy Atlas.



Không có nhận xét nào :
Đăng nhận xét