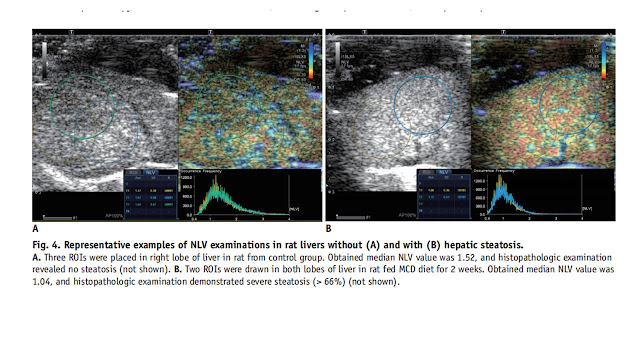
.jpg)
Normalized local variance (NLV) is a regional analysis used to quantify the homogeneity of the speckle patterns in B-mode images. NLV analyzes the spatial echo pattern of a grayscale image from the receiving echo signal amplitude within a certain region of interest (ROI) during normal ultrasound (US) examination. The system looks deeper into the US echo signal information, at more than 100 x higher resolution, and operates in the background with the raw data from this ROI.
Then, it extracts parameters and their complete probability distribution related to the “homogeneity” or “smoothness”of the structures reflecting the US beam sent by the machine into the body. The measured variance by this process is compared to a normalized variance of normal or reference liver tissue.
This is to standardize the variance of the echo signal of the micro-ROIs, which were automatically placed within the analytical ROI. The formula to calculate NLV is as follows:
According to this equation, when the speckle pattern is homogeneous, the NLV value is 1, which means that the amplitude distribution becomes the Rayleigh distribution. Scattering is diffuse reflection of ultrasound waves at interfaces that are typically equal to, or smaller than the wavelength. Rayleigh scattering occurs at interfaces that are several times smaller than the wavelength; thus, a homogeneous speckle pattern, like a fatty liver, is in agreement with the Rayleigh scattering distribution.
Furthermore, when inhomogeneous structures, like a blood vessel wall in a normal liver, are included in the analytical ROI, because other interactions of ultrasound waves occur in the liver tissue, such as specular reflection, the NLV is greater than 1.
Because NLV is based on the raw signal data of a grayscale that is collected before a scan converter, the gain for local intensity variance is independent.
--------
Normalized local variance (NLV) technique is an US quantification method that has recently been developed by Canon Medical Systems. The NLV technique is based on the statistical analysis of the echo amplitude obtained from the grayscale US images. Very small objects that are smaller than the US beam wavelength cause scattering and interference of the US beam, which generates a speckle pattern in the liver (22,23,24). Theoretically, the distribution of the echo amplitude in the liver approximates the Rayleigh distribution (24). However, in the real normal liver, small structures, such as vessel walls, which are larger than the US beam wavelength, increase the variance in the scattering, resulting in a heterogeneous speckle pattern, which deviates from the Rayleigh distribution. In contrast, in hepatic steatosis, the small structures become masked by the increased echogenicity of the surrounding hepatic parenchyma. Therefore, the real echo amplitude distribution of the steatotic liver approaches the theoretical Rayleigh distribution.
The NLV technique assesses the difference between the theoretical and real echo amplitude distribution, which is the reason we believe that it can be used for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis.
------
Chuẩn hóa biến đổi khu trú (NLV) là một phương pháp định lượng của siêu âm được Canon Medical Systems phát triển gần đây. Kỹ thuật NLV dựa trên phân tích thống kê về biên độ hồi âm thu được từ các hình thang độ xám của siêu âm. Các vật thể rất nhỏ nhỏ hơn bước sóng của chùm sóng âm gây ra sự tán xạ và giao thoa chùm sóng âm, tạo ra kiểu hình đốm trong gan (22,23,24). Về mặt lý thuyết, sự phân bố biên độ hồi âm trong gan xấp xỉ với phân bố Rayleigh (24). Tuy nhiên, ở gan bình thường, các cấu trúc nhỏ, chẳng hạn như thành mạch, lớn hơn bước sóng chùm sóng âm, làm tăng biến đổi tán xạ, dẫn đến kiểu hình đốm không đồng nhất, lệch khỏi phân bố Rayleigh. Ngược lại, trong gan nhiễm mỡ, các cấu trúc nhỏ bị che lấp bởi sự tăng hồi âm của nhu mô gan thấm mỡ xung quanh. Do đó, sự phân bố biên độ hồi âm thực của gan nhiễm mỡ tiệm cận với sự phân bố Rayleigh lý thuyết. Kỹ thuật NLV đánh giá được khác biệt giữa phân bố biên độ echo lý thuyết và thực tế, đó là lý do kỹ thuật NLV có thể được sử dụng để đánh giá gan nhiễm mỡ.


Không có nhận xét nào :
Đăng nhận xét